
Global warming is one of the most pressing environmental issues of the 21st century. It refers to the gradual rise in Earth’s average surface temperature caused mainly by human activities. The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial emissions have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere, trapping more heat and disturbing the planet’s natural balance. Scientists are more than 95% certain that global warming is primarily caused by human influence. Understanding its causes, impacts, and solutions is essential to ensure a sustainable future for the coming generations.
In daily life, we can already see its impact through rising temperatures, irregular rainfall, and changing seasons.
What is Global Warming?
Global warming is the long-term heating of Earth’s climate system observed since the pre-industrial period due to human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases. These gases include carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), nitrous oxide (N₂O), ozone (O₃), and water vapor. They act like a blanket around the Earth, absorbing heat and preventing it from escaping into space. As a result, Earth’s temperature rises, leading to melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and extreme weather patterns.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) confirms that Earth’s average surface temperature has risen by approximately 1.1°C since the late 19th century, with most of the warming occurring in the past 40 years. This temperature rise may seem small but has far-reaching and potentially irreversible impacts on natural and human systems.
Causes of Global Warming
1. Burning of Fossil Fuels
The massive use of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas is the primary cause of global warming. When burned for electricity, transportation, and industrial purposes, these fuels release large quantities of carbon dioxide — the most significant greenhouse gas — into the atmosphere. This CO₂ traps heat and prevents it from escaping, leading to a steady increase in global temperatures.

2. Deforestation
Forests act as carbon sinks by absorbing carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. However, rapid deforestation for agriculture, urbanization, and timber reduces this capacity. When trees are cut down, not only is carbon absorption lost, but the carbon stored in them is also released back into the atmosphere. As a result, deforestation directly accelerates global warming.
3. Intensive Farming
Modern agriculture, especially livestock farming, contributes significantly to methane and nitrous oxide emissions. Cattle and sheep release methane during digestion, while the use of nitrogen-based fertilizers emits nitrous oxide. Both gases are much more potent than carbon dioxide in trapping heat, making agriculture a key contributor to global warming.
4. Waste Disposal
Improper waste management practices, including landfills and incineration, produce harmful greenhouse gases such as methane. Decomposing organic waste in landfills emits methane, while burning waste materials releases both carbon dioxide and toxic pollutants into the atmosphere.
5. Mining and Industrial Activities
Mining and metal industries are responsible for around 5% of global greenhouse gas emissions. These industries rely heavily on fossil fuels for extraction, transport, and processing. The energy-intensive nature of these operations leads to massive carbon emissions.
6. Overconsumption
Overconsumption of natural resources and the increasing demand for goods contribute to more energy usage, transportation, and waste. This results in additional emissions from manufacturing and global trade, putting even more pressure on the environment.
This is something we experience every day through increased electricity use and fuel consumption.
Effects of Global Warming
1. Impact on Biodiversity
Global warming disturbs ecosystems and affects biodiversity worldwide. Rising temperatures and altered weather patterns force plants and animals to migrate or adapt quickly. Many species fail to cope with these changes, leading to extinction. According to the IPCC, a temperature rise of just 1.5°C could put 20–30% of all species at risk. The loss of biodiversity disrupts ecosystems, agriculture, and food chains, threatening ecological stability.
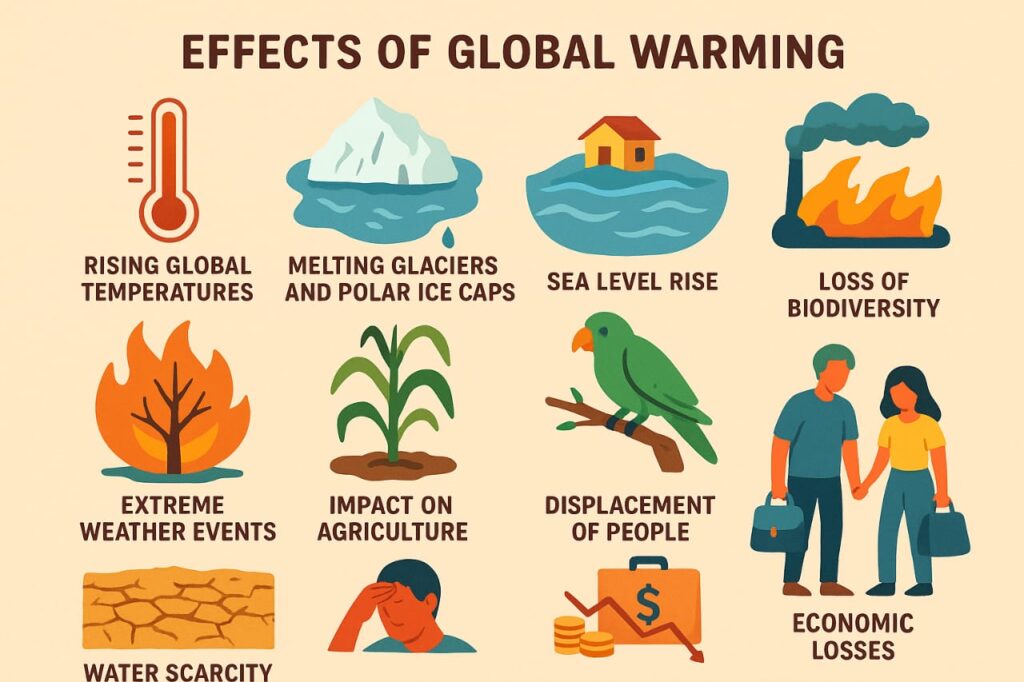
2. Impact on Oceans
Oceans are absorbing much of the excess heat caused by greenhouse gases, resulting in rising sea levels and ocean acidification. Polar ice caps and glaciers in Greenland and Antarctica are melting rapidly, causing global sea levels to rise. This threatens coastal communities and small island nations. Additionally, excess CO₂ makes oceans more acidic, harming coral reefs, shellfish, and marine life.
3. Impact on Humans
Humans are directly affected by global warming through food shortages, water scarcity, and health problems. Rising sea levels lead to flooding and displacement of populations, creating millions of climate refugees. By 2050, it is estimated that about 250 million people could be forced to migrate due to climate-related disasters. Extreme heat also increases the risk of diseases, reduces labor productivity, and affects mental well-being.
4. Impact on Weather Patterns
Global warming intensifies weather extremes such as droughts, floods, heatwaves, and hurricanes. Meteorologists have observed an increase in the frequency and intensity of storms in recent decades. For instance, warmer ocean temperatures strengthen tropical storms, turning them into more dangerous hurricanes. Droughts, on the other hand, lead to crop failure and water shortages, impacting agriculture and livelihoods globally.
Difference Between Global Warming and Climate Change
Though often used interchangeably, global warming and climate change are distinct terms. Global warming refers specifically to the rise in global average temperature due to greenhouse gas emissions. Climate change includes the broader range of changes affecting the planet’s climate — such as shifts in rainfall patterns, increased frequency of storms, and altered wind patterns.
The Greenhouse Effect Explained
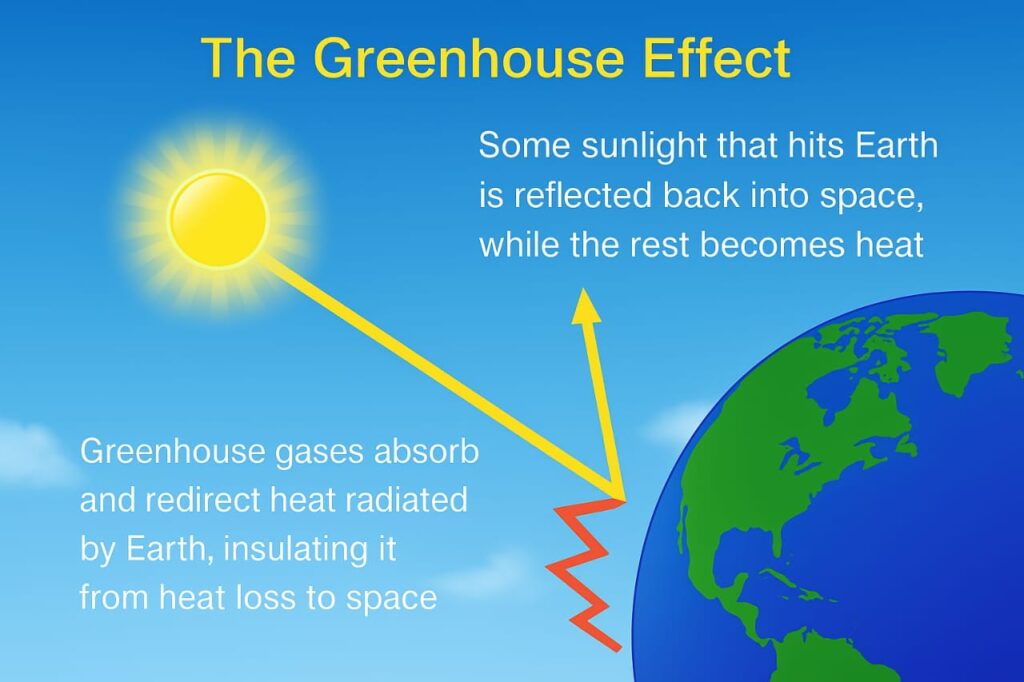
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that makes Earth habitable. The Sun’s energy reaches Earth, where part of it is absorbed and part reflected back into space. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap some of this outgoing heat, keeping the planet warm enough to support life. However, human activities have intensified this effect by releasing more greenhouse gases than the atmosphere can handle. The excessive trapping of heat leads to global warming.
Read more Deforestation
Global Warming and Extreme Weather

Global warming is strongly linked to extreme weather events. Rising temperatures contribute to longer heatwaves, intense droughts, heavier rainfall, and stronger hurricanes. For instance, the California drought of 2015, the worst in over 1,200 years, was intensified by global warming. Similarly, hurricanes like Katrina (2005) and Sandy (2012) gained strength due to warmer ocean waters. As global temperatures continue to rise, such catastrophic weather events will become more frequent and severe.
Prevention and Solutions
1. Shift to Renewable Energy
Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, geothermal, and biomass is crucial. These clean energy sources produce little or no greenhouse gases, helping to slow down global warming.
2. Improve Energy and Water Efficiency
Using energy-efficient appliances, LED lighting, and water-saving technologies can reduce overall energy demand. Small changes at the household level collectively make a significant difference.
3. Promote Sustainable Transportation
Encouraging public transport, cycling, carpooling, and the adoption of electric vehicles can drastically reduce carbon emissions from the transportation sector.
4. Green Building and Infrastructure
Constructing energy-efficient buildings and renovating older ones with better insulation and renewable power sources can minimize emissions. Urban green spaces also help absorb CO₂ and reduce heat islands.
5. Sustainable Agriculture and Forestry
Promoting eco-friendly farming practices, reducing fertilizer use, and preventing deforestation are vital steps. Reforestation and afforestation can help restore carbon-absorbing capacity and maintain ecological balance.
6. Responsible Consumption and Recycling
Mindful consumption—buying less, reusing materials, and recycling waste—helps cut down energy usage and reduces the burden on landfills. Every individual’s action matters in combating global warming.
Even small actions taken at an individual level can make a meaningful difference over time.
What Can Individuals Do?
Many people wonder whether their personal efforts can make a difference. The answer is yes. You can reduce your carbon footprint by conserving electricity and water, using public transport, choosing energy-efficient appliances, supporting environmental policies, and raising awareness about sustainable living.
Conclusion
Global warming is not just an environmental issue — it is a social, economic, and moral challenge. The planet’s health is directly linked to human survival and well-being. Immediate action is needed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, protect forests, and shift toward renewable energy. If we act decisively today, we can still limit the damage, restore ecological balance, and ensure that future generations inherit a livable Earth.
Global warming is not just an environmental issue but a shared responsibility. The choices we make today will shape the future of our planet.
Read more Earthquake
Read more Gardening
